Advantages of Using AAC Blocks
Facts about AAC

Autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) blocks are a widely used building material and are considered to be a suitable choice for many construction projects. Some of the benefits of using AAC blocks include their lightweight, thermal insulation properties, fire resistance, durability, sound insulation, ease of cutting and shaping, and environmental friendliness.
Overall, AAC blocks can be a good choice for many construction projects, but it is important to consult with a qualified building professional to ensure that they are the right choice (dimension and psi) for your specific needs.
Quick Facts about AAC
Autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) is a type of precast, foam concrete building material. It is made from cement, fine aggregate (such as sand), lime, water, gypsum and aluminum powder- an expansion agent that causes the fresh mixture to rise like bread dough. The material is cured in an autoclave, a pressurized chamber that cooks the mixture under high heat and steam. The resulting product is lightweight, strong, and thermally insulating. It is often used as an alternative to traditional hollow blocks in construction.
Invention of Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (AAC)
Autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) blocks were first developed by a Swedish architect and inventor named Johan Axel Eriksson in the 1920s. Eriksson was looking for a building material that was lightweight, fireproof, and energy-efficient. He began experimenting with different mixtures of cement, lime, and sand and eventually discovered that by adding an expansion agent to the mixture and curing it in an autoclave, he could produce a material that met all of his criteria. Eriksson's invention was patented in 1924 and the first AAC factory was built in Sweden the following year. Since then, AAC has been used in many countries as a building material. Read more
Safety of Using AAC Blocks
Autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) blocks are considered to be a safe building material for use in construction. They are made from natural materials, such as cement, sand, and water, and are produced under strict quality control standards. They have been widely used for many years in Europe and other parts of the world and have a track record of providing safe and durable buildings.
When used correctly and with proper design, installation and maintenance, AAC blocks are generally considered to be safe but it is always recommended to consult with a qualified building professional to ensure the safety of your building project.
Research on AAC During Earthquake
1. Germany
2. Japan
Features and Benefits of AAC Blocks
There are several advantages why autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) blocks may be used in construction projects:
Lightweight: AAC blocks are significantly lighter than traditional hollow blocks, making them easier to handle and transport.
Thermal insulation: AAC blocks have a lower thermal conductivity, making them an effective insulation material. This can help to reduce energy costs associated with heating and cooling a building.
Fire resistance: AAC blocks have a higher fire resistance than traditional hollow blocks. It has a fire rating of 4 hours.
Durability: AAC blocks are resistant to weathering and decay, and have a long service life.
Sound insulation: AAC blocks have good sound insulation properties, which can help to reduce noise transmission between rooms or between the interior and exterior of a building.
Easy to cut and shape: AAC blocks can be cut and shaped using standard carbide saw, making them easy to work with during construction.
Environmentally friendly: AAC blocks and panels are made from natural materials and use less energy to produce than hollow blocks.
Cost effective: AAC blocks have lower labor cost than other materials like hollow blocks. No more plastering, no more long curing time, and faster installation methodology and lesser rebars and mortars.
Accuracy: The panels and blocks made of autoclaved aerated concrete are produced to the exact sizes needed before leaving the factory. There is less need for on-site trimming. Since the blocks and panels fit so well together, there is less use of finishing materials such as mortar.
Long lasting: The life of this material is extended because it is not affected by harsh climates or extreme weather changes. It will not degrade under normal climate changes.
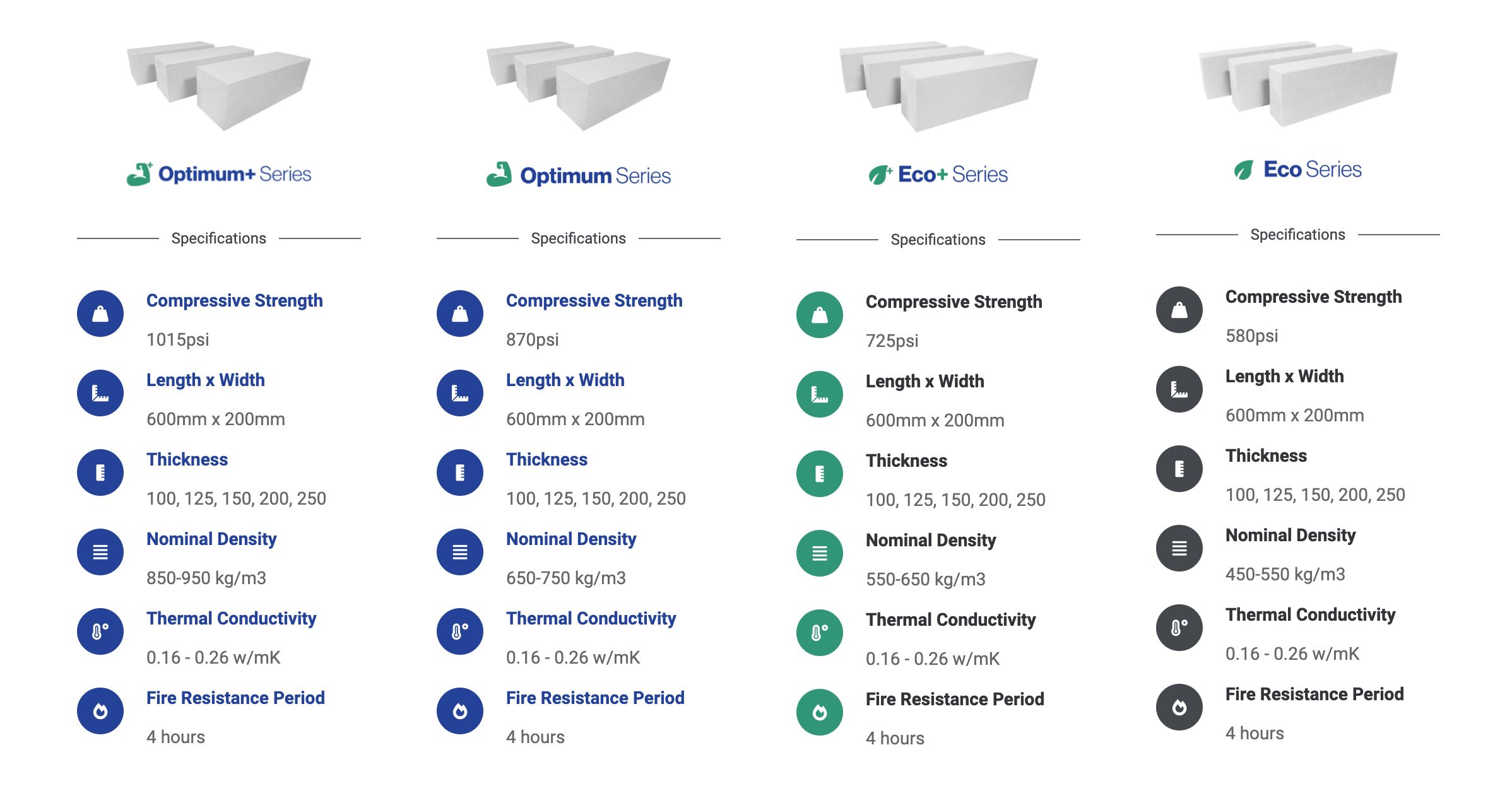
Specifications & Pricing
Compressive Strength: 580psi ~ 1,015psi
Thickness (mm): 100, 125, 150, 200, 250
Length x Width (mm): 600 x 200
Nominal Density: 450 ~ 950kg/m3
Fire Resistance: 4 Hours
AAC Blocks Pricing: 4 inch | 580psi AAC Blocks | ₱1,316/sqm
Where You Can Use AAC Blocks
Autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) blocks can be used in a variety of construction applications, including:
Residential construction: AAC blocks are commonly used in the construction of single-family homes, townhouses, and apartment buildings. They are particularly well-suited for use in load-bearing walls, partition walls, and exterior walls.
Commercial construction: AAC blocks are also used in the construction of commercial and industrial buildings, such as office buildings, warehouses, and factories. They can be used for load-bearing walls, partition walls, and exterior walls.
Interior walls: AAC blocks can be used to construct interior walls, such as walls separating rooms in a house or apartment, and walls between different levels in a building.
Exterior walls: AAC blocks can be used to construct exterior walls. They are suitable for use in both new construction and renovation projects.
Floor and roof systems: AAC panels can also be used in floor and roof systems, either as structural elements or as insulation.
Fire walls: AAC blocks have a high fire resistance, making them suitable for use in fire walls, which are designed to prevent the spread of fire within a building.
Prefabricated structures: AAC blocks can be used in prefabricated structures such as panels, which can be used to construct walls and floors in a faster and more efficient way.


Compositions of AAC (Autoclaved Aerated Concrete)
While ingredients may vary depending on manufacturer, AAC is generally made up of the following basic raw materials and elements:
Calcined Gypsum
Aluminum Powder
Cement
Water
Quartz Sand
Lime
Production of AAC
Steel molds are prepared to receive the fresh AAC. If reinforced AAC panels are to be produced, steel reinforcing cages are secured within the molds. After mixing, the slurry is poured into the molds.
When AAC is mixed and cast in forms, several chemical reactions take place that gives AAC its light weight (20% of the weight of concrete) and thermal properties. Aluminum powder reacts with calcium hydroxide and water to form hydrogen. The hydrogen gas foams and doubles the volume of the raw mix creating gas bubbles up to 3 millimetres (1⁄8 in) in diameter. The expansive agent creates small, finely dispersed voids in the fresh mixture, which increases the volume by about 50 percent in the molds within three hours. Read more